Bluetooth is an ideal, proven global standard for the “Connected Everything”: from the smartphone, to the smart home, to even the metaverse. Let’s dive into what makes Bluetooth so interesting and unique when compared to other technologies.
Introduction to Bluetooth
Even those people who are not specifically tech-savvy know that their smartphone, iPad, and PC have a feature called “Bluetooth”. In fact: every single smartphone comes with it on board. Today, it is impossible to find a smartphone without Bluetooth technology. The reason is simple. Some time ago, Google required all handset manufacturers who wanted to use Google apps on their phones to comply with their Android Compatibility Definition. Therefore, all manufacturers had to support 3G, GPS and Bluetooth (this has been made public as a result of a lawsuit between Oracle and Google). The iPhone as well comes with Bluetooth on board since its first generation.
Today, it is unthinkable to have a phone which does not support Bluetooth. Your AirPods or your wireless headphones are using Bluetooth technology to stream music from our phone to the headphones. When you get into your car, your phone automatically connects with it via Bluetooth. No matter whether you use an Apple Watch, Fitbit, or Garmin, your smartwatch synchronizes with your phone via Bluetooth LE.
No matter whether you use an Apple Watch, Bose headphones, or MESHLE flex controller: “everything is better with Bluetooth”

100% of all smartphones rely on Bluetooth technology today
Bluetooth SIG
Bluetooth was introduced in May 1998 — which is more than 23 years ago. This makes it only eight months younger than the popular Wi-Fi, which was introduced in September 1997.
In 2019 and 2020 respectively, 5 billion devices have been shipped with Bluetooth technology. This includes platform devices such as phones, tablets, and PCs but also peripheral devices such as headphones, wearables, or smart home devices.
According to Bluetooth SIG and ABI Research, in 2025 annual shipments will exceed six billion devices. This anticipated growth comes from peripheral devices such as wireless headphones, smart home devices, and sensors. By 2025 70% of all Bluetooth enabled device shipments will be peripheral devices.
By 2025, annual Bluetooth enabled device shipments will exceed six billion [per year]
ABI Research
Application Areas
The great thing about Bluetooth is, that it is not a single-use-case technology. Other wireless protocols are often useful for only one or two use cases: Zigbee — for example — is primarily utilized in building automation and in wireless sensor networks. With the recent introduction of Mesh, Bluetooth evolved into an ideal technology for building automation as well, which is, however, used in many more use-cases beyond that. Bluetooth’s applications range from IoT to wearables, medical, consumer electronics, smartphones, indoor-positioning and more. The Bluetooth Special Interest Group (Bluetooth SIG) — the organization which oversees and licenses Bluetooth technology — sorts the application areas into four specific solution areas:
- Audio Streaming
- Data Transfer
- Location Services
- Device Networks
Let’s look at each of them and how Bluetooth is impacting your life today or in the future.
Audio Streaming
As mentioned earlier, your AirPods or wireless Bose headphones use Bluetooth to stream your music in high definition from your smartphone. Audio streaming was one of Bluetooth’ first and as of 2020, it is Bluetooth largest application area. In 2020, a total of 1.1 billion audio streaming devices have been shipped.
Even though audio streaming was one of Bluetooth’ first real-world use cases, it is still an ever developing standard for audio streaming. Let’s mention a few innovations which Bluetooth introduced lately:
- LE Audio is a technology of Bluetooth with reduced power consumption while still supporting high-quality codecs and multi-stream audio.
- Multi-Stream is a feature which allow you to share music with friends by streaming audio from one device to multiple headphones or speakers.
- Audio Sharing will — for example — enable public spaces such as airports to stream public announcements directly to Bluetooth hearing assistance devices or Bluetooth headphones. An innovation for hearing-impaired people.
Data Transfer
Bluetooth is perfect for audio streaming, but it does not stop there. Your smartwatch — whether it is an Apple Watch or a Fitbit — is also using Bluetooth to transfer and synchronize data between your phone and the watch. In fact, 13 billion Bluetooth IoT devices will be in use in 2021 making it the leading technology for IoT. This includes wearables such as a smartwatch but also remote controls, PC accessories and a wide range of consumer electronics such as a smart toothbrush. Bluetooth will play a major role in the future of “Connected Everything” with an estimated 1.46 billion shipments of IoT devices in 2025 (ABI Research, 2021).
Bluetooth is the most important and relied upon technology for fitness trackers and telehealth wearables. It will enable more and more people to continuously monitor their vital signs and activity levels. In the future, wearables will be more than only smartwatches or fitness trackers. Just a few weeks ago, Facebook and Microsoft announced their intentions to focus on the metaverse. For this to work, smart AR glasses and VR headsets will be using Bluetooth to connect to your environment and your smartphone. Bluetooth will also be a crucial technology for smart industrial manufacturing, warehousing, and asset tracking.
Location Services
Bluetooth is also a great technology for locating other devices and measuring distances. Earlier in 2021, Apple introduced the AirTag. The AirTag is a Bluetooth LE powered device which makes it easy to locate lost items such as your keys. However, the majority of use cases are outside the consumer market. Bluetooth SIG is looking forward to a large growth in the indoor navigation niche. For example, to help you find products in the retail store faster. Bluetooth’s location services also allow you to use your smartphone as a secure digital key to unlock the door of a car sharing vehicle, your office building, or smart home.
Device Networks
Smart home and commercial lighting use cases are driving an exceptional growth to the Bluetooth Device Networks devices. From 2021 to 2025 the annual shipment of these devices is estimated to grow by 4.4x annually. In 2021, this category is consisting of smart appliances (35%), smart lighting (27%), sensors (19%), smart blinds (4%), thermostats (3%), and also door locks (2%) (ABI Research, 2020)
Commercial connected lighting is a large growth market which the Bluetooth SIG is growing into. The Bluetooth SIG is also actively collaborating with the DALI Alliance to ensure an interoperability between all lighting components.
Bluetooth Keeps Innovating
For over 23 years, Bluetooth is a tried and tested technology. A variety of different product categories and industries are utilizing Bluetooth technology, which allows Bluetooth to still grow in a fast pace. What makes it so popular? Bluetooth was introduced in 1997. Since then, it has evolved continuously into a global industry standard which is supported by 36,645 companies worldwide. The latest major improvements were Bluetooth Low Energy (or in short: BLE), Bluetooth Mesh and Bluetooth 5. Let’s look at what makes them so interesting.
Bluetooth Low Energy
The technology of Bluetooth Low Energy (Bluetooth LE or BLE) was originally developed by Nokia under the Name Wibree and then integrated into Bluetooth 4.0 as Bluetooth Low Energy. As the name reveals, Bluetooth LE uses considerably less power than the classic Bluetooth while still providing a similar range. With the introduction of BLE, Bluetooth suddenly became a relevant and interesting technology for battery-powered devices and small and low-cost devices such as wearables or IoT sensors. These devices were — thanks to the Bluetooth ecosystem — immediately compatible with phones, tablets, and PCs. Bluetooth Low Energy is supporting different profiles for different use cases. The use cases are ranging from health care profiles, sport and fitness profiles, sensor profiles, lately the Mesh specifications and a LE Audio profile.
Bluetooth 5
Bluetooth 5 was an important update to enable Bluetooth for the Internet of Things. It introduced a high-speed and a long-range mode to increase the data rate to up to 2Mbps or increase the range — with data rates of 125kbs or 500kbs.
Bluetooth 5 is marketed solely under the “Bluetooth 5” brand. Nevertheless, there have already been further refinements and updates: Bluetooth 5.1 for location services such as indoor positioning, Bluetooth 5.2 for audio streaming, and Bluetooth 5.3 for improved latency, interference, battery, and security.
Bluetooth Mesh
Bluetooth Mesh is another crucial progression of Bluetooth. In the past, the limited range was a big disadvantage. In theory, Bluetooth 4.0 LE has a maximum range of 100 meters. (measured free field and outdoors). In reality, Bluetooth 4 has a range of 10 to 25 meters (realistic indoor use). Because of this, Bluetooth was not the ideal technology for IoT. The introduction of Bluetooth Mesh changed this.
Mesh networks are networks where every device is communicating with every other device within range. Every device is passing data on to every other device within range and is thereby acting as a repeater.
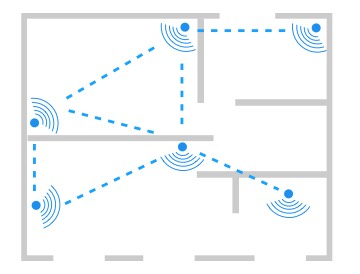
Without a mesh network, devices are communicating only with each other directly. For example: your smartphone streams music directly to your Bluetooth headset (point-to-point). Another example is the setup of traditional Wi-Fi. Your phone connects directly to the Wi-Fi router. If different devices communicate between each other, the router acts as a middlemen or gateway between them.
Bluetooth Mesh does not have a central router or gateway. Each device (also called a node) communicates with each other and passes on all traffic it receives. Every Bluetooth mesh device acts simultaneously as an endpoint and a router/repeater. Thereby, the range of a Bluetooth Mesh network improves with every new Bluetooth Mesh device added to the network.
Bluetooth is Future-Proof
The combination of all previously mentioned advantages make Bluetooth a future-proof and exciting technology for current and future applications:
- Energy optimized Bluetooth LE
- High-performance Bluetooth 5
- Bluetooth Mesh without gateways
- Proven Bluetooth Ecosystem with 100% of phones supporting Bluetooth
The combination of Bluetooth 5 and Bluetooth Mesh solved the most important remaining factor: range. Bluetooth 5 makes device to device connections between 40 and 400 meters possible. By setting up a Bluetooth Mesh network, these ranges improve and multiply accordingly. This makes Bluetooth 5 Mesh an ideal technology even for large building automations or even smart city installations.
Connected Everything
In the future, wearables will evolve into more than just smartwatches or smart rings. Smart health devices will evolve, which will all rely on Bluetooth to sync and distribute data. In the future, builders will equip buildings and smart homes with an abundance of cheap sensors and smart actuators. Bluetooth Mesh enables them to be fully interoperable without any additional gateway or router, while building upon the mature and trusted Bluetooth ecosystem of more than 36,000 manufacturers and billions of devices in use.
In addition, Bluetooth Mesh is the only mesh technology which brings with it the proven, interoperability with 100% of all smartphones, tablets, Macs, and most PCs. As the future progresses, we will control our environment not only with a smartphone app but also through smart AR glasses or VR headsets. These AR and VR devices will come with and rely upon Bluetooth to connect with your smartphone and also directly with other devices in your environment. (By the way: the current Oculus Quest 2 VR headset comes with Bluetooth). If we go one step further, even upcoming brain computer interfaces like Elon Musk’s Neuralink will be equipped with Bluetooth.
Here is one example: if there’s a fire alarm, the closest firebox will send an alert via Bluetooth directly to your VR headset (or Neuralink) to warn you. The same is true for your burglar alarm, doorbell and more.
The future will connect everything with each other. The only technology capable of this — without routing all data through an additional gateway, router, or a foreign cloud — is Bluetooth.


