Everyone knows Bluetooth as a technology to stream music, synchronize wearables or control smart home appliances. When it comes to mesh, however, things are not that clear anymore. In this non-technical overview, we want to look at what a mesh network is and look at the rudiments of Bluetooth Mesh.
What is a Mesh Network?
Before we explain what a mesh network is, let’s look at how we transfer data between different devices if there is no mesh network. Let’s look at point-to-point connections and star networks.
Point-to-Point
If you are streaming music from your smartphone to your wireless headphones, your phone connects directly with your wireless headphones using Bluetooth. You don’t need any other device like a router or gateway. This is why you can stream music via Bluetooth even if you are outdoors and offline — at the top of a mountain in Norway. Experts call this a point-to-point connection. Two devices or nodes are directly communicating with each other.
Networks
Star network
Let’s look at a different example: you returned home from your trip to the Norwegian mountains. Now you want to stream music with your Sonos Wi-Fi speakers. You have no direct connection with your Sonos speaker via Bluetooth. Rather, your phone connects to your Wi-Fi router at home. Moreover, all your thirteen Sonos speakers have an active connection with your Wi-Fi router. Therefore, your Wi-Fi router acts as a central hub to which every device or node has an active connection with. If you send a command from your phone, this command is passed through the central hub (your Wi-Fi router), from where this command gets passed-on to the addressed devices.
There is one disadvantage of this type of network: the central hub is a single point of failure. Let’s say your Wi-Fi router breaks, this means you cannot stream any music at all. Technical jargon calls this type of network a star network or star typology.
Other networks
A point-to-point connection is great if there are only two devices communicating with each other. One example is music streaming. Another example might be connecting a wireless computer mouse with your laptop. As soon you connect multiple devices with each other, you create a network of some sort. The most common example is the previously mentioned Wi-Fi router, which symbolizes a star network. Besides that, also other types of networks exist. A bus network connects multiple devices directly with each other with one cable. This however works only with a very limited number of devices. A tree network connects multiple star networks with each other (via a bus cable with similar limitations). Then there are grid networks, which you might know from how electricity is distributed via power grids.
When we are looking at homes, offices or buildings, a star topology is the most common form of network. In a typical smart home, all smart actuators and sensors have a direct connection with your Wi-Fi router or smart home hub. In larger buildings, the devices are usually wired and merge somewhere in a server room, where they are connected to a central hub.
Mesh network
The central hub, whether it is a router, a switch, or a smart home hub, makes things complicated. The larger the network becomes, the more expensive and complex it gets.
In a traditional network, all devices must have a wired or wireless connection to the central hub. Traditionally, this is being done by hard-wiring all nodes — which include actuators, sensors, switches, etc. — to a server room. Hard-wiring an entire building is complex, labor- and material-intensive, and thus costly. A wireless setup quickly reaches its range limit, especially in larger buildings. This is where the benefits of a mesh network become clear.
Mesh networks can bring wireless connectivity to large spaces and buildings far more simply and affordable than ever before. Let’s look at what a mesh network is.
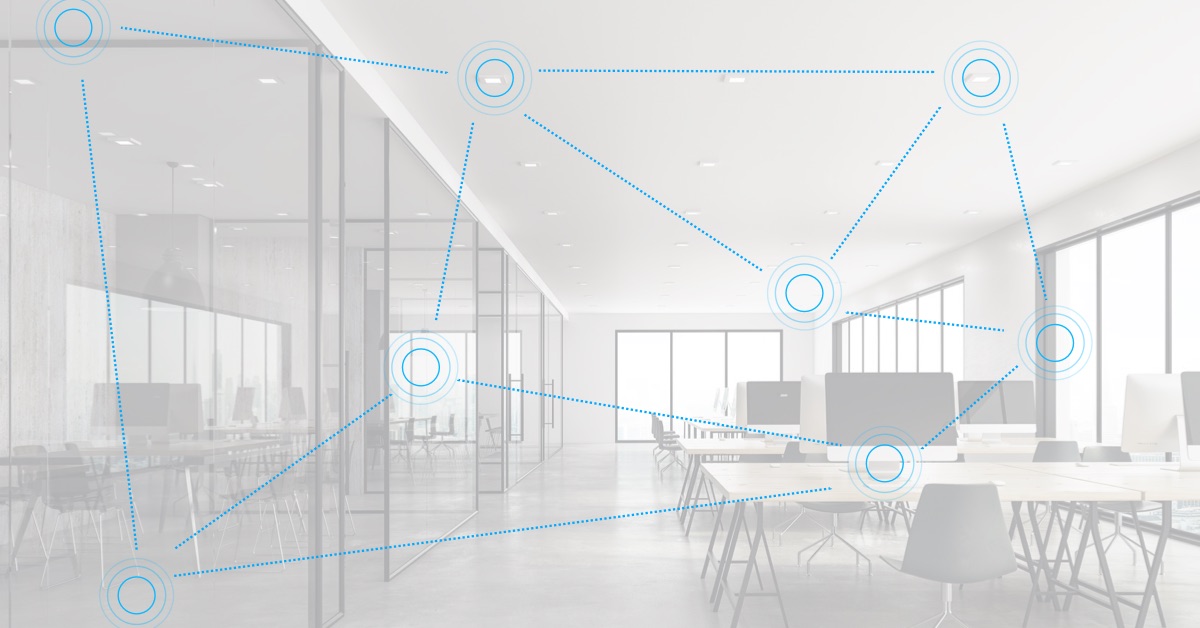
A mesh network is describing a network where devices — which are also called nodes — are connected directly and non-hierarchically to one another. In a fully connected mesh network, all nodes are connected with each other. Each node can communicate directly with every other node. However, in a mesh network, not necessarily all nodes are connected with each other. Some nodes might be out of range to communicate directly with each other. In this case, nodes — which have no direct connection — communicate through other nodes with each other. This means, every node in a mesh network acts as an endpoint and simultaneously also as a repeater. Adding one device in a network and within range to another device extends the range of both devices. If you add more devices, the range, and coverage of the network extends accordingly.
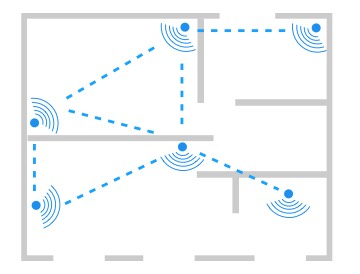
Bluetooth Mesh
Star- or tree typology networks are well established and standardized. This has not been the case for mesh networks. Some technology companies and manufacturers developed proprietary wireless mesh networks on their own, but until recently a common standard and interoperability did not exist.
In 2017, Bluetooth SIG — the organization which oversees and licenses Bluetooth technology — introduced a standardized mesh networking protocol. Bluetooth Mesh brings with it a proven and mature ecosystem and compatibility with 100% of all smartphones globally, which makes a central hub truly redundant.
This means Bluetooth Mesh comes with all the advantages of Bluetooth, including:
- Energy optimized Bluetooth LE
- High-performance Bluetooth 5
- Proven Bluetooth Ecosystem with 100% of phones supporting Bluetooth
Use-Case: Smart Home
One exciting use case is the smart home. Previously, it has been an expensive undertaking to build a smart home. Typically, every switch, actuator, and sensor is hard-wired with a highly complex bus system. This results in significant costs for planning, wiring, and installing the system — usually in the tens to hundreds of thousands of Euros or Dollars. As an alternative, some people retrofit their homes with a Wi-Fi, ZigBee or Z-Wave solution — which all rely on central hubs and standalone repeater.
A smart home based on Bluetooth Mesh does not need expensive planning, cables, or experts who program the system. One configures the Bluetooth Mesh network easy as anything with a smartphone (for example with the MESHLE app). All devices in the home establish a local Bluetooth 5 Low-Energy mesh network. There’s excellent coverage in every spot of the home without a need for a central hub, gateway, repeater and without a server room. Compared to hard-wired smart home systems, this massively cuts cost and complexity.
Résumé
Bluetooth Mesh delivers significant benefits over traditional star networks. It simplifies the smart building by reducing complexity and wiring to an absolute minimum. With a growing standardization of Bluetooth Mesh (often referred to as the Qualified Bluetooth Mesh) it will have a massive impact on the IoT and smart home industry for many years to come. Even though the focus lies on the lighting industry at the moment, we’ll see a massive adaption in the smart home, and even the smart city of the future.
By the way, if you want to test a Bluetooth Mesh network yourself, the easiest way is to try one of our MESHLE flex LED controller. Multiple MESHLE flex controllers automatically form a Bluetooth Mesh network, which you can control and automate with our MESHLE app from your smartphone.